Indicators on Roar Solutions You Need To Know
Indicators on Roar Solutions You Need To Know
Blog Article
The Best Strategy To Use For Roar Solutions
Table of ContentsAll About Roar SolutionsWhat Does Roar Solutions Mean?Fascination About Roar Solutions
In order to protect installations from a potential explosion a technique of analysing and classifying a potentially hazardous area is required. The purpose of this is to make sure the appropriate choice and installation of equipment to inevitably prevent an explosion and to make sure safety of life.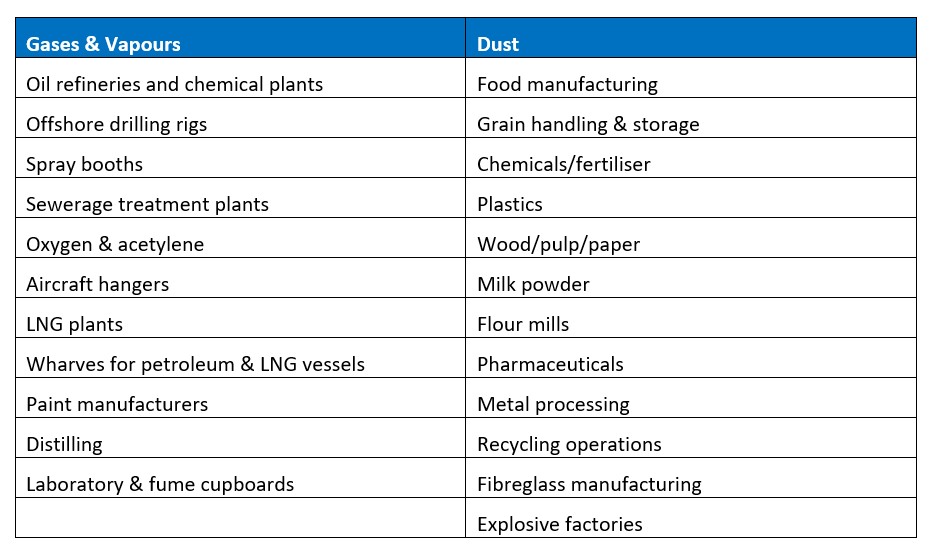
(https://medium.com/@thomascarrillo4740/about)
No tools ought to be set up where the surface area temperature level of the tools is higher than the ignition temperature of the given threat. Below are some usual dirt hazardous and their minimum ignition temperature. Coal Dust 380C 225C Polythene 420C (thaws) Methyl Cellulose 420C 320C Starch 460C 435C Flour 490C 340C Sugar 490C 460C Grain Dirt 510C 300C Phenolic Resin 530C > 450C Aluminium 590C > 450C PVC 700C > 450C Residue 810C 570C The possibility of the hazard existing in a concentration high enough to cause an ignition will differ from location to area.
In order to categorize this risk an installment is separated right into areas of threat relying on the quantity of time the unsafe exists. These areas are described as Areas. For gases and vapours and dusts and fibers there are 3 zones. Zone 0 Area 20 A harmful atmosphere is highly most likely to be present and might be existing for extended periods of time (> 1000 hours per year) and even continuously Area 1 Zone 21 A hazardous environment is feasible yet unlikely to be existing for extended periods of time (> 10 450 C [842 F] A category of T6 suggests the minimum ignition temperature level is > 85 C [185 F] Harmful location electric devices possibly made for usage in greater ambient temperatures. This would suggested on the score plate e.g. EExe II C T3 Ta + 60C( This suggests at 60C ambient T3 will not be exceeded) T1 T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6 T2 T2, T3, T4, T5, T6 T3 T3, T4, T5, T6 T4 T4, T5, T6 T5 T5, T6 T6 T6 A T Class score of T1 implies the maximum surface temperature generated by the tool at 40 C is 450 C. Assuming the associated T Class and Temperature level ranking for the devices are proper for the area, you can constantly make use of an instrument with a more rigorous Department score than required for the location. There isn't a clear response to this concern sadly. It really does rely on the kind of devices and what repair work need to be executed. Equipment with certain examination treatments that can't be done in the area in order to achieve/maintain third party rating. Must return to the manufacturing facility if it is before the equipment's service. Field Repair By Authorised Employee: Complicated testing might not be called for however details treatments may need to be complied with in order for the tools to preserve its 3rd party score. Authorized workers should be utilized to execute the work correctly Repair service need to be a like for like replacement. New element must be considered as a straight replacement calling for no unique testing of the tools after the fixing is full. Each piece of equipment with an unsafe ranking need to be reviewed individually. These are outlined at a high level below, however, for even more comprehensive details, please refer straight to the standards.
10 Easy Facts About Roar Solutions Explained
The tools register is a thorough database of equipment records that includes a minimum set of fields to determine each thing's place, technological specifications, Ex lover category, age, and environmental information. This info is critical for monitoring and handling the devices efficiently within harmful areas. On the other hand, for regular or RBI tasting inspections, the grade will be a mix of Thorough and Close assessments. The proportion of Thorough to Close inspections will certainly be established by the Devices Threat, which is examined based on ignition danger (the probability of a source of ignition versus the chance of a combustible environment )and the harmful area category
( Area 0, 1, or 2). This variant will additionally influence the resourcing demands for work prep work. When Whole lots are specified, you can establish tasting strategies based on the sample dimension of each Lot, which describes the variety of arbitrary equipment items to be evaluated. To establish the called for example size, two elements need to be assessed: the size of the Lot and the group of examination, which suggests the degree of effort that must be used( lowered, typical, or enhanced )to the assessment of the Lot. By incorporating the category of inspection with the Whole lot dimension, you can then establish the appropriate rejection criteria for a sample, meaning the permitted variety of damaged things found within that sample. For even more information on this procedure, please describe the Power Institute Guidelines. The IEC 60079 common suggests that the maximum period between evaluations ought to not surpass three years. EEHA assessments will additionally be performed beyond RBI campaigns as part of scheduled maintenance and equipment overhauls or repair services. These examinations can be credited toward the RBI example dimensions within the affected Great deals. EEHA assessments are performed to identify mistakes in electric devices. A weighted scoring system is necessary, as a solitary item of equipment might have several faults, each with varying degrees of ignition threat. If the combined rating of both examinations is less than twice the fault rating, the Whole lot is regarded acceptable. If the Great deal is still considered undesirable, it must go through a full assessment or validation, which may set off more information more stringent examination methods. Accepted Whole lot: The causes of any type of mistakes are recognized. If an usual failing setting is discovered, added tools might require inspection and repair service. Mistakes are identified by intensity( Safety and security, Stability, Housekeeping ), ensuring that urgent issues are assessed and attended to without delay to minimize any type of effect on safety and security or procedures. The EEHA data source ought to track and record the lifecycle of mistakes along with the rehabilitative activities taken. Applying a robust Risk-Based Examination( RBI )technique is crucial for guaranteeing compliance and security in managing Electric Devices in Hazardous Locations( EEHA) (eeha certificate). Automated Mistake Rating and Lifecycle Administration: Effortlessly take care of mistakes and track their lifecycle to enhance assessment precision. The introduction of this support for risk-based assessment even more reinforces Inspectivity's position as a best-in-class remedy for regulative compliance, in addition to for any type of asset-centric inspection usage instance. If you are interested in finding out more, we welcome you to request a presentation and discover how our option can change your EEHA monitoring processes.
The Single Strategy To Use For Roar Solutions

In terms of eruptive threat, a hazardous location is an environment in which an explosive environment exists (or may be anticipated to be present) in amounts that require special safety measures for the construction, installment and usage of equipment. Roar Solutions. In this short article we check out the obstacles encountered in the work environment, the risk control actions, and the required competencies to function securely
These compounds can, in certain problems, create eruptive environments and these can have major and terrible repercussions. Many of us are acquainted with the fire triangular get rid of any kind of one of the 3 components and the fire can not take place, however what does this mean in the context of dangerous locations?
In many instances, we can do little concerning the degrees of oxygen in the air, yet we can have substantial influence on sources of ignition, as an example electric tools. Harmful locations are documented on the unsafe area classification drawing and are determined on-site by the triangular "EX-SPOUSE" indicator. Here, amongst various other crucial info, areas are divided right into three types depending on the risk, the likelihood and duration that an eruptive atmosphere will certainly exist; Area 0 or 20 is considered the most hazardous and Area 2 or 22 is regarded the least.
Report this page